'AtlasClientV2#purgeEntitiesByGuids' method is used to hard delete the entities. ‘purge’ operation is supported only on soft deleted entities.
Example
atlasClient.purgeEntitiesByGuids(guidsSet);
Find the below working application.
Create atlas-application.properties file under src/main/resources folder.
atlas-application.properties
atlas.client.readTimeoutMSecs=30000 atlas.client.connectTimeoutMSecs=30000
Define HardDeleteEntityByIds class.
HardDeleteEntityByIds.java
package com.sample.app.entity;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import org.apache.atlas.AtlasClientV2;
import org.apache.atlas.AtlasServiceException;
import org.apache.atlas.model.instance.AtlasEntity;
import org.apache.atlas.model.instance.AtlasEntityHeader;
import org.apache.atlas.model.instance.EntityMutationResponse;
import org.apache.atlas.model.typedef.AtlasEntityDef;
import org.apache.atlas.model.typedef.AtlasStructDef.AtlasAttributeDef;
import org.apache.atlas.model.typedef.AtlasTypesDef;
public class HardDeleteEntityByIds {
private static final String TYPE_NAME = "DemoType22";
private static void createType(AtlasClientV2 atlasClient) throws AtlasServiceException {
AtlasAttributeDef attributeDef1 = new AtlasAttributeDef();
attributeDef1.setName("a");
attributeDef1.setTypeName("int");
attributeDef1.setCardinality(AtlasAttributeDef.Cardinality.SINGLE);
attributeDef1.setIsIndexable(true);
attributeDef1.setIsUnique(false);
AtlasAttributeDef attributeDef2 = new AtlasAttributeDef();
attributeDef2.setName("b");
attributeDef2.setTypeName("int");
attributeDef2.setCardinality(AtlasAttributeDef.Cardinality.SINGLE);
attributeDef2.setIsIndexable(true);
attributeDef2.setIsUnique(false);
AtlasEntityDef atlasEntityDef = new AtlasEntityDef();
atlasEntityDef.setName(TYPE_NAME);
atlasEntityDef.setCreatedBy("Krishna");
atlasEntityDef.setUpdatedBy("krishna");
atlasEntityDef.setDescription("Represent a laptoo specification");
atlasEntityDef.setAttributeDefs(Arrays.asList(attributeDef1, attributeDef2));
Set<String> superTypes = new HashSet<>();
superTypes.add("DataSet");
atlasEntityDef.setSuperTypes(superTypes);
AtlasTypesDef atlasTypesDef = new AtlasTypesDef();
atlasTypesDef.getEntityDefs().add(atlasEntityDef);
atlasClient.createAtlasTypeDefs(atlasTypesDef);
}
private static EntityMutationResponse createEntities(AtlasClientV2 atlasClient) throws AtlasServiceException {
// Defining entity1
AtlasEntity atlasEntity1 = new AtlasEntity();
atlasEntity1.setTypeName(TYPE_NAME);
atlasEntity1.setAttribute("a", 10);
atlasEntity1.setAttribute("b", 20);
atlasEntity1.setAttribute("qualifiedName", "HardDeleteEntityByIds_DEMO1");
atlasEntity1.setAttribute("name", "HardDeleteEntityByIds_DEMO1");
// Defining entity2
AtlasEntity atlasEntity2 = new AtlasEntity();
atlasEntity2.setTypeName(TYPE_NAME);
atlasEntity2.setAttribute("a", 11);
atlasEntity2.setAttribute("b", 21);
atlasEntity2.setAttribute("qualifiedName", "HardDeleteEntityByIds_DEMO2");
atlasEntity2.setAttribute("name", "HardDeleteEntityByIds_DEMO2");
// Defining entity3
AtlasEntity atlasEntity3 = new AtlasEntity();
atlasEntity3.setTypeName(TYPE_NAME);
atlasEntity3.setAttribute("a", 11);
atlasEntity3.setAttribute("b", 21);
atlasEntity3.setAttribute("qualifiedName", "HardDeleteEntityByIds_DEMO3");
atlasEntity3.setAttribute("name", "HardDeleteEntityByIds_DEMO3");
AtlasEntity.AtlasEntitiesWithExtInfo entitesToCreate = new AtlasEntity.AtlasEntitiesWithExtInfo();
entitesToCreate.setEntities(Arrays.asList(atlasEntity1, atlasEntity2, atlasEntity3));
return atlasClient.createEntities(entitesToCreate);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws AtlasServiceException, IOException {
AtlasClientV2 atlasClient = new AtlasClientV2(new String[] { "http://localhost:21000" },
new String[] { "admin", "admin" });
createType(atlasClient);
EntityMutationResponse entityMutationesponse = createEntities(atlasClient);
List<AtlasEntityHeader> entitiesCreated = entityMutationesponse.getCreatedEntities();
List<String> guids = new ArrayList<>();
for (AtlasEntityHeader atlasEntityHeader : entitiesCreated) {
guids.add(atlasEntityHeader.getGuid());
}
System.out.println("Deleting the objects.....");
atlasClient.deleteEntitiesByGuids(guids);
System.out.println(
"Please enter any input to hard delete the entities. Before this, you can go and validate the created/deleted entities of type "
+ TYPE_NAME);
readInput();
System.out.println("Hard deleting the objects.....");
atlasClient.purgeEntitiesByGuids(new HashSet<>(guids));
}
private static void readInput() throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
br.readLine();
}
}
Run above application, you will see below messages in console.
Deleting the objects..... Please enter any input to hard delete the entities. Before this, you can go and validate the created/deleted entities of type DemoType22
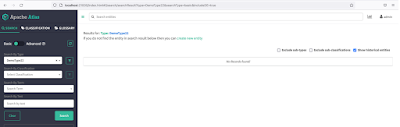
Go to Atlas UI and query for the type ‘DemoType22’ and select the check box ‘Show historical entities’ to see soft deleted entities.
Now go back to the Java application console, and type something to proceed with hard deletion.
Perform the search again on type ‘DemoType22’, you will observe that the entities are no more in the system.
Previous Next Home

No comments:
Post a Comment