You can run the tests inside a suite parallel by specifying thread count and setting parallel attribute to the value ‘tests’.
Example
<suite name="Parallel tests" parallel="tests" thread-count="2">
<test name="ParallelTests1">
<classes>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest1"></class>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest2"></class>
</classes>
</test>
<test name="ParallelTests2">
<classes>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest3"></class>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest4"></class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
In the above snippet, I specified thread count as 2. Test classes in ‘ParallelTests1’ are executed by one thread, and test classes in ‘ParallelTests2’ are executed by other thread.
Find the below working application.
ParallelTest1.java
package com.sample.app.tests;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ParallelTest1 {
@Test
public void a() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest1_a is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void b() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest1_b is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void c() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest1_c is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void d() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest1_d is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void e() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest1_e is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
ParallelTest2.java
package com.sample.app.tests;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ParallelTest2 {
@Test
public void a() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest2_a is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void b() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest2_b is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void c() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest2_c is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void d() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest2_d is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void e() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest2_e is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
ParallelTest3.java
package com.sample.app.tests;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ParallelTest3 {
@Test
public void a() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest3_a is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void b() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest3_b is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void c() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest3_c is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void d() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest3_d is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void e() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest3_e is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
ParallelTest4.java
package com.sample.app.tests;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class ParallelTest4 {
@Test
public void a() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest4_a is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void b() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest4_b is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void c() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest4_c is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void d() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest4_d is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
@Test
public void e() {
System.out.println("ParallelTest4_e is executed by : " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
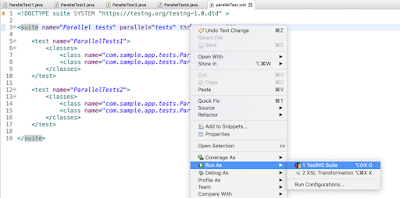
Create ‘parallelTest.xml’ file in the same package where the test classes are defined.
<!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "https://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd" >
<suite name="Parallel tests" parallel="tests" thread-count="2">
<test name="ParallelTests1">
<classes>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest1"></class>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest2"></class>
</classes>
</test>
<test name="ParallelTests2">
<classes>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest3"></class>
<class name="com.sample.app.tests.ParallelTest4"></class>
</classes>
</test>
</suite>
How to run the test suite?
Right click on parallelTest.xml -> Run As -> TestNG Suite.
You will get below messages in console.
ParallelTest1_a is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest3_a is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest3_b is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest3_c is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest1_b is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest3_d is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest3_e is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest1_c is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest4_a is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest1_d is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest4_b is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest4_c is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest4_d is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest1_e is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest4_e is executed by : TestNG-tests-2 ParallelTest2_a is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest2_b is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest2_c is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest2_d is executed by : TestNG-tests-1 ParallelTest2_e is executed by : TestNG-tests-1