Write a generic method that takes a enum name as input and return an enumeration constant that matches the string without being case sensitive.
Signature
public static <T extends Enum<T>> T byNameInsensitiveCase(final Class<T> enumType, final String name)
An enum constant in Java is a special type of variable that represents a fixed set of values. Enum constants are declared within an enum type and can be used to define named constants for a specific type or category.
Use Cases of Enum Constants:
1. Representing Predefined Values: Enum constants are often used to define a fixed set of options or states within an application. For example, days of the week, months of the year, colors, etc.
2. Type Safety: Enums provide type safety, ensuring that only valid values can be assigned to variables of that type.
3. Switch Statements: Enums are commonly used in switch statements to handle multiple cases elegantly.
4. Configuration Options: Enums can be used to represent configuration options or settings in applications.
5. State Machines: Enum constants are useful for defining states in finite state machines, making state transitions clearer and more manageable.
Find the below working application.
EnumUtils.java
package com.sample.util;
public class EnumUtils {
/**
*
* @param <T>
* @param enumClazz - Enum class object
* @param name - name of the enum constant
* @return the enum constant that matches to given name. Throws
* {@link IllegalArgumentException} if no enum matches to the given
* name.
*/
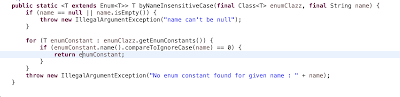
public static <T extends Enum<T>> T byNameInsensitiveCase(final Class<T> enumClazz, final String name) {
if (name == null || name.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name can't be null");
}
for (T enumConstant : enumClazz.getEnumConstants()) {
if (enumConstant.name().compareToIgnoreCase(name) == 0) {
return enumConstant;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No enum constant found for given name : " + name);
}
}
EnumByNameDemo.java
package com.sample.app;
import com.sample.util.EnumUtils;
public class EnumByNameDemo {
private static enum Month {
JANUARY(1, "31 Days"), FEBRUARY(2, "28 or 29 Days"), MARCH(3, "31 Days"), APRIL(4, "30 days"),
MAY(5, "31 Days"), JUNE(6, "30 Days"), JULY(7, "31 Days"), AUGUST(8, "31 Days"), SEPTEMBER(9, "30 Days"),
OCTOBER(10, "31 Days"), NOVEMBER(11, "30 Days"), DECEMBER(12, "31 Days");
int num;
String msg;
Month(int num, String msg) {
this.num = num;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String toString() {
return this.name() + " is the " + num + " month and has " + msg;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Month month = EnumUtils.byNameInsensitiveCase(Month.class, "auGUst");
System.out.println(month);
}
}
Output
AUGUST is the 8 month and has 31 Days
Previous Next Home
No comments:
Post a Comment