Step 1: Define a Bucket instance.
Bandwidth limit = Bandwidth.classic(5, Refill.greedy(10, Duration.ofSeconds(30)));
Bucket bucket = Bucket.builder().addLimit(limit).build();
Above snippet define a bucket with capacity 5 (It can store 5 tokens maximum), and refill the tokens in greedy manner (10 tokens in 30 seconds duration). For example refill "10 tokens per 1 second" will add 1 token per each 100 millisecond, in other words refill will not wait 1 second to regenerate whole bunch of 10 tokens.
The three refills bellow do refill of tokens with same speed:
a. Refill.greedy(600, Duration.ofMinutes(1));
b. Refill.greedy(10, Duration.ofSeconds(1));
c. Refill.greedy(1, Duration.ofMillis(100));
Step 2: Apply rate limiting on the methods that you are interested.
private static void getResource() {
if (bucket.tryConsume(1)) {
System.out.println("Resource accessed....");
return;
}
System.err.println("Too Many Requests, all the tokens consumed");
}
‘getResource’ method try to get a token before permitting access to the resource. if it got the token then the resource will be accessed successfully, else some error message is printed to the console.
Find the below working application.
HelloWorld.java
package com.sample.app;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import io.github.bucket4j.Bandwidth;
import io.github.bucket4j.Bucket;
import io.github.bucket4j.Refill;
public class HelloWorld {
private static Bucket bucket;
private static void getResource() {
if (bucket.tryConsume(1)) {
System.out.println("Resource accessed....");
return;
}
System.err.println("Too Many Requests, all the tokens consumed");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Bandwidth limit = Bandwidth.classic(5, Refill.greedy(10, Duration.ofSeconds(30)));
bucket = Bucket.builder().addLimit(limit).build();
while (true) {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
getResource();
}
}
}
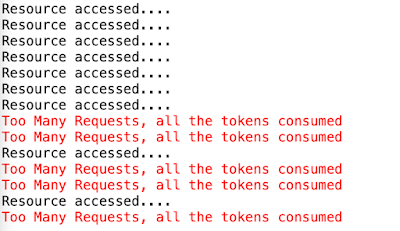
Sample output
No comments:
Post a Comment