Using SecurityManager#getClassContext we can get the name of calling class that invokes given method.
Signature
protected Class[] getClassContext()
Returns the current execution stack as an array of classes. The length of the array is the number of methods on the execution stack. The element at index 0 is the class of the currently executing method, the element at index 1 is the class of that method's caller, and so on.
Find the below working application.
StringUtil.java
package com.sample.app.util;
public class StringUtil {
public static void printHi() {
Class<?> clazz = AppUtil.getCallingClass();
System.out.println("Hi!!!!!");
System.out.println("This method is called by " + clazz);
}
}
AppUtil.java
package com.sample.app.util;
public class AppUtil {
private static ClassContextSecurityManager SECURITY_MANAGER;
private static final class ClassContextSecurityManager extends SecurityManager {
protected Class<?>[] getClassContext() {
return super.getClassContext();
}
}
private static ClassContextSecurityManager getSecurityManager() {
if (SECURITY_MANAGER == null) {
synchronized (AppUtil.class) {
if (SECURITY_MANAGER == null) {
SECURITY_MANAGER = new ClassContextSecurityManager();
}
}
}
return SECURITY_MANAGER;
}
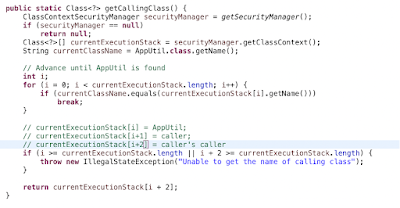
public static Class<?> getCallingClass() {
ClassContextSecurityManager securityManager = getSecurityManager();
if (securityManager == null)
return null;
Class<?>[] currentExecutionStack = securityManager.getClassContext();
String currentClassName = AppUtil.class.getName();
// Advance until AppUtil is found
int i;
for (i = 0; i < currentExecutionStack.length; i++) {
if (currentClassName.equals(currentExecutionStack[i].getName()))
break;
}
// currentExecutionStack[i] = AppUtil;
// currentExecutionStack[i+1] = caller;
// currentExecutionStack[i+2] = caller's caller
if (i >= currentExecutionStack.length || i + 2 >= currentExecutionStack.length) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable to get the name of calling class");
}
return currentExecutionStack[i + 2];
}
}
App.java
package com.sample.app;
import com.sample.app.util.StringUtil;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringUtil.printHi();
}
}
Output
Hi!!!!! This method is called by class com.sample.app.App
You may like
How to call base class method from subclass overriding method?
Can an interface extend multiple interfaces in Java?
instanceof operator behavior with interface and class
Call the main method of one class from other class using reflection
No comments:
Post a Comment