Parameterized tests are used to run a test method multiple times using different arguments.
To work with parameterized tests, you should add below dependency.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>${junit-jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
How to define a parameterized test?
You can define parameterized tests using @ParameterizedTest annotation.
For example, below snippet demonstrates a parameterized test that uses the @ValueSource annotation to specify a String array as the source of arguments.
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = { "Krishna", "Ram", "Gopi" })
void welcomeUserTest(String userName) {
assertEquals("Hello " + userName, welcomeUser(userName));
}
ParameterizedTests1.java
package com.sample.app;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.ParameterizedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.params.provider.ValueSource;
public class ParameterizedTests1 {
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = { "Krishna", "Ram", "Gopi" })
void welcomeUserTest(String userName) {
assertEquals("Hello " + userName, welcomeUser(userName));
}
private static String welcomeUser(String userName) {
return "Hello " + userName;
}
}
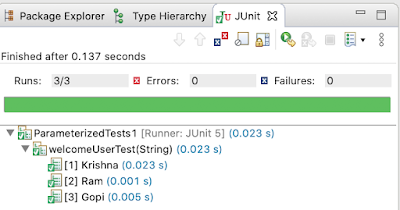
Run above class, you will see that the test case ‘welcomeUserTest’ executed three times.
@ValueSource is one of the simplest possible way to pass arguments to parameterized tests.
The following types of literal values are supported by @ValueSource.
a. short
b. byte
c. int
d. long
e. float
f. double
g. char
h. boolean
i. java.lang.String
j. java.lang.Class
No comments:
Post a Comment