'java.util.Collection' class provides
'removeIf' method to remove all the elements of this collection that satisfy
the given predicate. This method returns true, if any element is removed from
the collection.
Test.java
The definition of ‘removeIf’ method looks
like below.
default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(filter);
boolean removed = false;
final Iterator<E> each = iterator();
while (each.hasNext()) {
if (filter.test(each.next())) {
each.remove();
removed = true;
}
}
return removed;
}
As you see above snippet, removeIf method
uses the collection iterator to traverse the elements. If the element matches
to the predicate, then it is removed from the collection using iterator
'remove' method. If iterator do not support removal of elements, then
UnsupportedOperationException is thrown.
Find the below working example.
Employee.java
package com.sample.app.model; public class Employee { private int id; private String firstName; private String lastName; public Employee(int id, String firstName, String lastName) { this.id = id; this.firstName = firstName; this.lastName = lastName; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + "]"; } }
Test.java
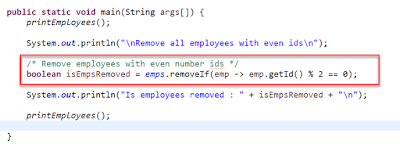
package com.sample.app; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import com.sample.app.model.Employee; public class Test { private static List<Employee> emps = new ArrayList<>(); static { loadEmployees(); } private static void loadEmployees() { Employee emp1 = new Employee(1, "Krishna", "Gurram"); Employee emp2 = new Employee(2, "Joel", "Chelli"); Employee emp3 = new Employee(3, "Gopi", "Battu"); Employee emp4 = new Employee(4, "Janaki", "Sriram"); Employee emp5 = new Employee(5, "Janaki", "Maj"); emps.addAll(Arrays.asList(emp1, emp2, emp3, emp4, emp5)); } private static void printEmployees() { emps.stream().forEach(System.out::println); } public static void main(String args[]) { printEmployees(); System.out.println("\nRemove all employees with even ids\n"); /* Remove employees with even number ids */ boolean isEmpsRemoved = emps.removeIf(emp -> emp.getId() % 2 == 0); System.out.println("Is employees removed : " + isEmpsRemoved + "\n"); printEmployees(); } }
Run Test.java, you can able to see below
messages in console.
Employee [id=1, firstName=Krishna, lastName=Gurram] Employee [id=2, firstName=Joel, lastName=Chelli] Employee [id=3, firstName=Gopi, lastName=Battu] Employee [id=4, firstName=Janaki, lastName=Sriram] Employee [id=5, firstName=Janaki, lastName=Maj] Remove all employees with even ids Is employees removed : true Employee [id=1, firstName=Krishna, lastName=Gurram] Employee [id=3, firstName=Gopi, lastName=Battu] Employee [id=5, firstName=Janaki, lastName=Maj]
No comments:
Post a Comment