In this
post, I am going to explain how to communicate to active directory over SSL. It
is three-step process.
1.
Get
ssl certificate from Active directory.
2.
Import
SSL certificate to cacerts file.
3.
Write
JNDI program to communicate over ssl.
How to Get SSL certificate from Active
Directory?
a.
Install
the Active Directory Certificate Services
b.
Exporting
the LDAPS Certificate.
a. Install the Active Directory Certificate
Services
a. Log in to
your Active Directory server as an administrator.
b. Click
Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
c. In the
Roles Summary section, click Add Roles.
Press Next, On the Select Server Roles
page, select the Active Directory Certificate Services check box. Click Next
twice.
On the Select Role Services page, select
the Certification Authority check box, and then click Next.
On the Specify Setup Type page, click
Enterprise, and then click Next.
On the
Specify CA Type page, click Root CA, and then click Next.
On the Set Up Private Key and Configure
Cryptography for CA pages, you can configure optional configuration settings,
including cryptographic service providers. However, the default values should
be fine. Click Next twice.
In the
Common name for this CA box, type the common name of the CA, and then click
Next.
On the Set Validity Period page, accept
the default values or specify other storage locations for the certificate
database and the certificate database log, and then click Next.
After verifying the information on the
Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
Review the
information on the results screen to verify that the installation was
successful.
b. Exporting the LDAPS Certificate.
1. Click
Start, type mmc and then click OK.
2. Click
File and then click Add/Remove Snap-in.
3. Click
Certificates and then click Add.
4. In
Certificates snap-in select Computer account and then click Next.
e. In Select Computer, if you are
working at the LDAP server requiring the certificate, select Local. Otherwise,
select Another computer and click Browse to locate the LDAP server requiring
the certificate.
Once you have the correct computer
selected, click OK and then click Finish.
In the console tree, expand Certificates
(<computer>)
In the certificates console of a
computer that contains a certificate that can be used for Server
Authentication, right-click the certificate, click All Tasks, and then click
Export.
Press Next.
Press Next.
Press Next.
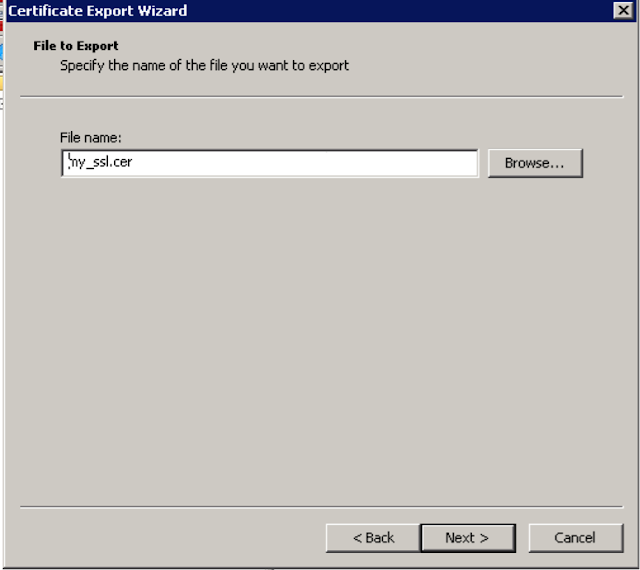
Give the
file name as ‘my_ssl.cer’.
Press next, Finish.
Step 2: Import the Server Certificate
a. For an application server to trust
your directory's certificate, the certificate must be imported into your Java
runtime environment.
The default keystore file is called
cacerts and it lives in the jre\lib\security sub-directory of your Java
installation. Java provides keytool command to import certificates.
keytool -importcert -keystore
.\jre\lib\security\cacerts -file server-certificate.crt
Ex:
keytool -importcert -keystore "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_45\jre\lib\security\cacerts" -file "C:\Users\vipadmin.VIPDEVEW\Downloads\my_ssl.cer"
b. keytool will prompt you for a
password. The default keystore password is changeit.
c. When prompted Trust this certificate?
[no]: enter yes to confirm the key import:
C:\Users>keytool -importcert -keystore "C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_45\jre\li
b\security\cacerts" -file "C:\Users\vipadmin.VIPDEVEW\Downloads\my_ssl.cer"
Enter keystore password:
Owner: CN=vip16-win8-p1-d.vipdevew.com
Issuer: CN=vip16-win8-p1-d.vipdevew.com
Serial number: 5eee1692d723749d47b54faa1edf671b
Valid from: Thu Jun 02 16:08:49 IST 2016 until: Fri Jun 02 05:30:00 IST 2017
Certificate fingerprints:
MD5: 21:2F:10:20:51:A6:A4:47:18:E2:72:EE:78:34:B3:06
SHA1: C3:A2:AF:B5:AE:3E:A2:88:E6:B9:9B:34:70:4D:D7:40:C1:98:7C:7C
SHA256: 5C:30:AD:9B:93:7E:BF:7D:BE:42:A3:B9:BB:D9:71:BC:B3:E3:E5:70:FE:
74:7D:D1:C8:27:FE:24:4C:C8:20:18
Signature algorithm name: SHA1withRSA
Version: 3
Extensions:
#1: ObjectId: 2.5.29.37 Criticality=false
ExtendedKeyUsages [
serverAuth
]
#2: ObjectId: 2.5.29.15 Criticality=false
KeyUsage [
Key_Encipherment
Data_Encipherment
]
Trust this certificate? [no]: yes
Certificate was added to keystore
Step 3: Following Java program get all
the groups information usind ldaps.
import java.util.Properties; import javax.naming.Context; import javax.naming.NamingException; import javax.naming.directory.DirContext; import javax.naming.directory.InitialDirContext; public class DirectoryUtil { private final static String FACTORY = "com.sun.jndi.ldap.LdapCtxFactory"; private final static String PROVIDER_URL = "ldaps://localhost:636"; private static final Properties properties = new Properties(); private static String adminDN = "DC=example,DC=com"; private static String adminPassword = "password "; static { initProperties(); } private static void initProperties() { properties.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, FACTORY); properties.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, PROVIDER_URL); properties.put("com.sun.jndi.ldap.connect.pool", "true"); properties.put(Context.SECURITY_PRINCIPAL,adminDN); properties.put(Context.SECURITY_CREDENTIALS, adminPassword); //properties.put(Context.SECURITY_PROTOCOL, "ssl"); } public static DirContext getContext() throws NamingException { DirContext context = new InitialDirContext(properties); return context; } }
private final static String PROVIDER_URL =
"ldaps://localhost:636";
As you see
above statement, I am using ldaps, localhost. If you generated ssl certificate
on name abc.com, replace localhost with abc.com.
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Objects; import java.util.Optional; import javax.naming.NamingEnumeration; import javax.naming.NamingException; import javax.naming.directory.Attribute; import javax.naming.directory.Attributes; import javax.naming.directory.DirContext; import javax.naming.directory.SearchControls; import javax.naming.directory.SearchResult; /* get Distinguished name of user */ public class Test { /** * Return all group names (return the name mapped to cn) * * @param context * @param baseDN * @return */ static Optional<List<String>> getAllGroupNames(DirContext context, String baseDN) { if (Objects.isNull(context)) { System.out.println("context shouldn't be null"); return Optional.empty(); } List<String> groupNames = new ArrayList<>(); SearchControls ctls = new SearchControls(); String[] attrIDs = { "distinguishedName" }; ctls.setReturningAttributes(attrIDs); ctls.setSearchScope(SearchControls.SUBTREE_SCOPE); NamingEnumeration<?> answer; try { answer = context.search(baseDN, "(objectclass=group)", ctls); while (answer.hasMore()) { SearchResult searchResult = (SearchResult) answer.next(); Attributes attrs = searchResult.getAttributes(); Attribute cnAttr = attrs.get("distinguishedName"); NamingEnumeration<?> values = cnAttr.getAll(); while (values.hasMoreElements()) { groupNames.add(values.next().toString()); } } } catch (NamingException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); return Optional.empty(); } return Optional.of(groupNames); } public static void main(String[] args) throws NamingException { DirContext context = DirectoryUtil.getContext(); String baseDN = "CN=Users,DC=vipdevew,DC=com"; Optional<List<String>> groupsTmp = getAllGroupNames(context, baseDN); List<String> groups = groupsTmp.get(); for(String group : groups){ System.out.println(group); } } }
Compile the
program.
javac
Test.java
Run the
program by specifying cacerts file.
java
-Djavax.net.ssl.trustStore="C:\Program
Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_45\jre\lib\security\cacerts" Test
Reference


















No comments:
Post a Comment