A
Blocking Queue is just like a queue with additional functionality
like wait for the queue to become non-empty while removing and wait
for the queue to become free while adding element to the queue.
A
thread trying to perform dequeue operation on empty BlockingQueue,
blocked until this queue has some items.
A
thread trying to perform enqueue operation on completely filled
BlockingQueue, blocked until this queue makes some space to store
data.
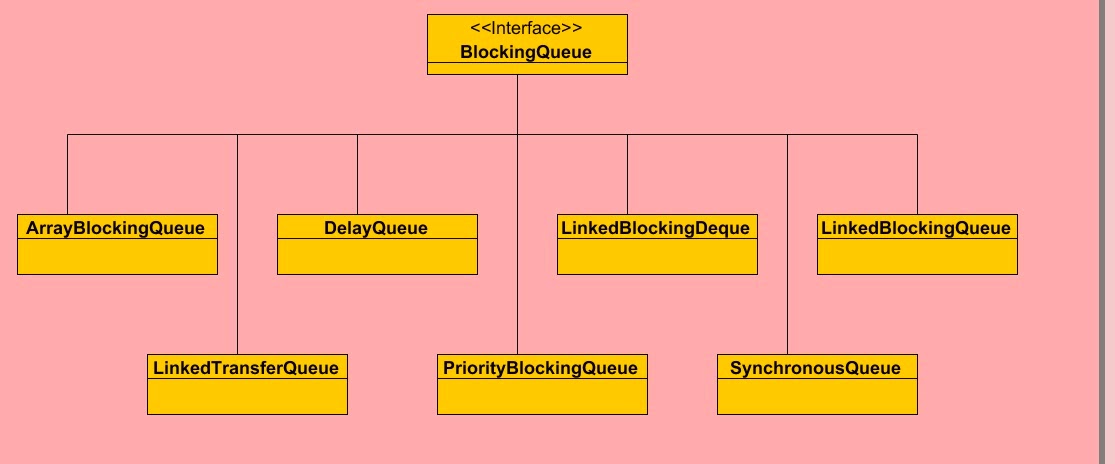
Classes
ArrayBlockingQueue, DelayQueue, LinkedBlockingDeque,
LinkedBlockingQueue, LinkedTransferQueue, PriorityBlockingQueue,
SynchronousQueue implement BlockingQueue interface.
BlockingQueue
provides 4 set of methods to insert, remove and examine the element
in Queue. Each set of methods behave differently, if they are unable
to perform the operation at given point of time like throwing
exception, waiting infinitely, waiting finitely or by returning
special value.
| Throws exception | Special value | Blocks | Times out | |
| Insert | add(e) | offer(e) | put(e) | offer(e, time, unit) |
| Remove | remove() | poll() | take() | poll(time, unit) |
| Examine | element() | peek() |
I
am going to explain all the 4 categories of methods by using the
below scenario.
Let
us assume, there is 2 producer threads and 1 consumer thread, a
BlockingQueue of size 10. Producer threads produce and place the item
in BlockingQueue, where as consumer thread consumes the items.
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class Producer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue<Integer> queue; Producer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } @Override public void run(){ int i=0; while(true){ synchronized(queue){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":" + i); queue.add(i); i++; } } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class Consumer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue queue; Consumer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } public void run(){ while(true){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":"); System.out.println(queue.remove()); } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; public class ThrowsException { public static void main(String args[]){ BlockingQueue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3); Producer p1 = new Producer(q); Producer p2 = new Producer(q); Consumer con = new Consumer(q); Thread t1 = new Thread(p1); t1.setName("P1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(p2); t2.setName("P2"); Thread t3 = new Thread(con); t3.setName("Con"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
Sample Output
P1:0 Con:P1:1 P1:2 P1:3 P2:0 Exception in thread "Con" java.util.NoSuchElementException at java.util.AbstractQueue.remove(AbstractQueue.java:117) at Consumer.run(Consumer.java:13) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745) Exception in thread "P2" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98) at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312) at Producer.run(Producer.java:17) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745) Exception in thread "P1" java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full at java.util.AbstractQueue.add(AbstractQueue.java:98) at java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue.add(ArrayBlockingQueue.java:312) at Producer.run(Producer.java:17) at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
2. Special value
boolean offer(E e)
offer method returns true, if the element was added to this queue, else false.
E poll()
Return the head of this queue, or null if this queue is empty.
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class Producer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue<Integer> queue; Producer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } @Override public void run(){ int i=0; while(true){ synchronized(queue){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":" + i); System.out.println(queue.offer(i)); i++; } } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; public class Consumer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue queue; Consumer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } public void run(){ while(true){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":"); System.out.println(queue.poll()); } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; public class SpecialValue { public static void main(String args[]){ BlockingQueue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3); Producer p1 = new Producer(q); Producer p2 = new Producer(q); Consumer con = new Consumer(q); Thread t1 = new Thread(p1); t1.setName("P1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(p2); t2.setName("P2"); Thread t3 = new Thread(con); t3.setName("Con"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
Sample Output
P1:0 Con:true P1:1 true P2:0 true 0 P2:1 Con:true P2:2 1 true P2:3 Con:false P2:4 true P2:5 false P2:6 false 0 P2:7 false P2:8 false Con:P2:9 1 true Con:P2:10 2 true Con:P2:11 4 true Con:9 Con:10 Con:11 Con:null Con:null ...
3. Blocks
void put(E e) throws InterruptedException
Inserts the specified element into this queue, waiting if necessary for space to become available.
E take() throws InterruptedException
Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, waiting if necessary until an element becomes available.
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.logging.Level; import java.util.logging.Logger; public class Producer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue<Integer> queue; Producer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } @Override public void run(){ int i=0; while(true){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":" + i); try { queue.put(i); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { Logger.getLogger(Producer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } i++; } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.logging.Level; import java.util.logging.Logger; public class Consumer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue queue; Consumer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } public void run(){ while(true){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":"); try { System.out.println(queue.take()); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { Logger.getLogger(Consumer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; public class Blocks { public static void main(String args[]){ BlockingQueue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3); Producer p1 = new Producer(q); Producer p2 = new Producer(q); Consumer con = new Consumer(q); Thread t1 = new Thread(p1); t1.setName("P1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(p2); t2.setName("P2"); Thread t3 = new Thread(con); t3.setName("Con"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
Sample Output
P1:0 P1:1 P1:2 P1:3 Con:0 P1:4 Con:1 P1:5 Con:2 P1:6 Con:3 P1:7 Con:4 P1:8 Con:5 P1:9 etc.,
4. Times out
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.logging.Level; import java.util.logging.Logger; public class Producer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue<Integer> queue; Producer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } @Override public void run(){ int i=0; while(true){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":" + i); try { queue.offer(i,2, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { Logger.getLogger(Producer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } i++; } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import java.util.logging.Level; import java.util.logging.Logger; public class Consumer implements Runnable{ BlockingQueue queue; Consumer(BlockingQueue q){ queue = q; } public void run(){ while(true){ System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName() +":"); try { System.out.println(queue.poll(1, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { Logger.getLogger(Consumer.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex); } } } }
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue; import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue; public class TimeOut { public static void main(String args[]){ BlockingQueue q = new ArrayBlockingQueue(3); Producer p1 = new Producer(q); Producer p2 = new Producer(q); Consumer con = new Consumer(q); Thread t1 = new Thread(p1); t1.setName("P1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(p2); t2.setName("P2"); Thread t3 = new Thread(con); t3.setName("Con"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
Sample Output
P1:0 Con:P2:0 P2:1 0 Con:P2:2 1 P1:1 Con:P2:3 0 Con:P1:2 2 … … …
No comments:
Post a Comment